The Truth About Quantum Mechanics

Quantum mechanics is one of the most fascinating and mind-bending topics in modern science. Although it is often considered complex and challenging, with a little effort, anyone can begin to grasp its fundamental concepts. Here, we will explore quantum mechanics in an easy-to-understand way, diving into its key theories and experiments.
What Is Quantum Mechanics?
Quantum mechanics is the branch of physics that studies the behavior of subatomic particles and the nature of energy. Unlike classical physics, which allows us to predict the past and future of objects with precision, quantum mechanics deals with probabilities and uncertainties.
In the quantum world, particles do not exist in well-defined states until they are observed. When observed, these quantum particles "collapse" into well-defined forms, becoming particles that we can measure.
Key Theories of Quantum Mechanics
1. Quantum Entanglement (EPR Paradox)
Quantum entanglement is one of the most intriguing phenomena in quantum mechanics. It states that two or more particles can become interconnected in such a way that the state of one particle instantaneously affects the state of the other, no matter how far apart they are.
For instance, if one particle is rotating clockwise, the other will rotate counterclockwise, maintaining a connection across vast distances. This principle applies only to quantum particles and not to objects in the macroscopic (everyday) world. If proven universally true, it would suggest that everything in the universe is fundamentally interconnected.
2. Wave-Particle Duality
Wave-particle duality is the concept that every particle, such as an electron, exhibits both wave-like and particle-like properties simultaneously.
- When we observe an electron, it appears as a particle.
- When we do not observe it, it behaves like a wave, spreading out across space.
This duality is mysterious but has been experimentally verified. It suggests that the act of observation plays a critical role in determining the state of quantum particles.
3. The Role of Consciousness in the Universe
Some scientists theorize that consciousness itself plays a role in shaping reality. According to this idea, the universe is not an objective reality but is instead created by our thoughts and perceptions.
This theory implies that our thoughts and consciousness determine our reality. While not universally accepted, researchers like Henry Stapp have explored this idea, suggesting that our thoughts have profound implications for our lives.
4. Time Does Not Exist
In the quantum world, time may not exist as we perceive it. Physicist Carlo Rovelli, in his book The Order of Time, argues that time in the quantum realm does not flow linearly.
In our everyday experience, time seems to move forward, but in the quantum world, time can move randomly, and some theories even suggest that it is possible to describe the quantum world without time at all.
5. Parallel Universes
The theory of parallel universes, also known as the Many-Worlds Interpretation, posits that every possible outcome of a situation exists in a separate universe.
For example, in one universe, you might become a scientist, while in another, you might be an artist. Hugh Everett, who proposed this theory, suggests that there could be universes where no one ever dies, and every imaginable possibility plays out in a parallel dimension.
6. Future Events Affecting the Past
One of the most shocking ideas in quantum mechanics is that future events can influence the past. This is demonstrated by the Double-Slit Experiment, a foundational experiment in quantum physics.
The Double-Slit Experiment
- Case 1: No Observer - An electron is fired at a screen with two slits. When not observed, the electron behaves like a wave, creating an interference pattern on the screen.
- Case 2: With an Observer - When a conscious observer observes the electron, it behaves like a particle and does not create an interference pattern.
- Case 3: Sudden Observation - If the electron is initially unobserved (producing a wave-like behavior) and an observer suddenly starts watching, the electron retroactively behaves like a particle. This suggests that the act of observation in the future can alter the past state of the particle.

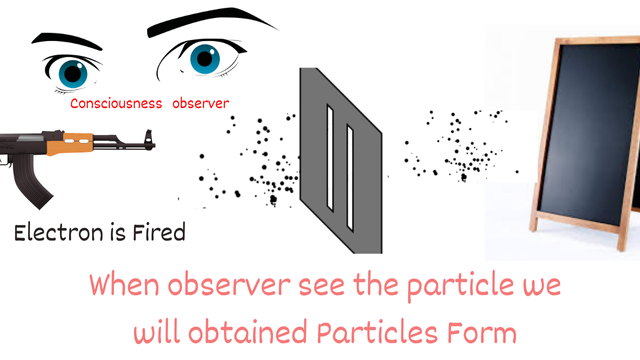

This experiment challenges our conventional understanding of cause and effect and highlights the strange nature of the quantum world.
Why Study Quantum Mechanics?
Understanding quantum mechanics is not just about unraveling the mysteries of the universe; it also has practical implications. Quantum principles are at the heart of groundbreaking technologies such as quantum computing, cryptography, and teleportation.
Conclusion
Quantum mechanics challenges our fundamental understanding of reality, time, and existence. From the bizarre behavior of particles to the possibility of parallel universes, it invites us to think beyond the boundaries of classical physics.
Together, let's decode the mysteries of the universe!
Explore Prep4IISER's unique programs and New Year offers to kickstart your journey.
For More Visit prep4iiser.com